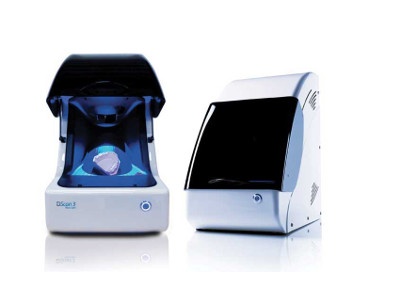
Dental 3D scanners for labs: Hardware selection and guide

3D scanners for dental labs
Dentistry is almost as old as mankind itself, but the practice is no stranger to new and exciting technologies.
Bit by bit, dentists are beginning to replace traditional methods with digital dentistry. This involves the use of digital capture, digital design, and digital production technologies to improve the speed, accuracy, and profitability of dental practice.
A key part of digital dentistry is the use of 3D scanners, which capture 3D shapes using a combination of cameras and light projection before transferring the result to a computer.
Not all dental 3D scanners work in the same way, though. Intraoral dental scanners scan directly inside a patient’s mouth and are used in a clinical setting, while desktop scanners capture dental models or impressions (negative imprints of a patient’s teeth and gums) and are usually used in a laboratory setting.
This article provides a simple dental scanners comparison, shortlisting a selection of market-leading desktop scanners. We also explain how dental scanning works and why it is so useful.

Top 11 dental 3D scanners for labs in 2023
| Brand | Product | Accuracy | Country | Price
Approximate starting prices based on supplier-provided information and public data. Prices may vary by region, over time and do not include additional products or services (taxes, shipping, accessories, training, installation, …).
| |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shining 3D Dental
Product data validated by the manufacturer.
| AutoScan DS-MIX | 0.007 mm | China | $ 9,999 | Quote |
| Medit | T500 | 0.07 mm | South Korea | $ 12,000 | Quote |
| Dentsply Sirona | inEos X5 | – | United States | $ 15,000 | Quote |
| EGSolutions | DScan 3 | – | Italy | $ 15,000 | Quote |
| imes-icore | I3Dscan color HR | – | Germany | $ 15,000 | Quote |
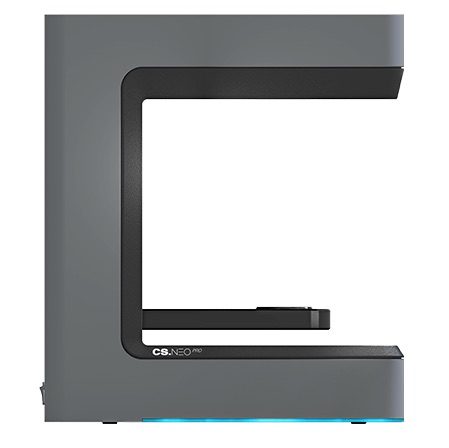
| CADstar | CS.Neo Pro | – | Austria | $ 19,000 | Quote |
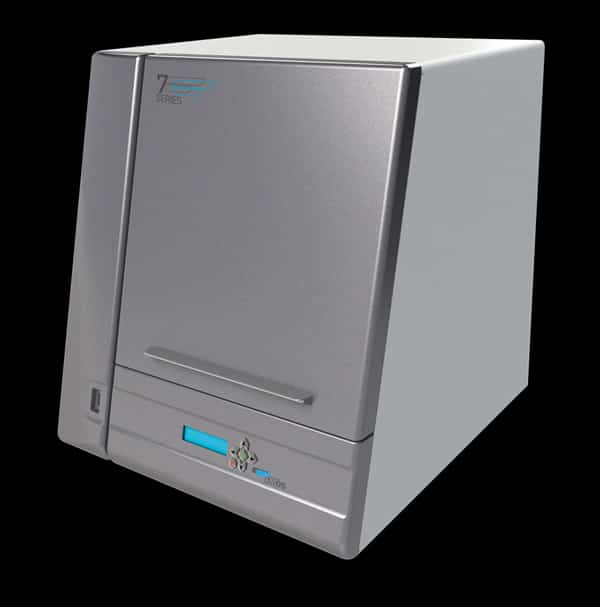
| dental wings | 7Series | 0.015 mm | – | $ 20,000 | Quote |
| Zfx | Zfx Evolution Plus | – | Germany | $ 20,000 | Quote |
| AmannGirrbach | Ceramill Map 200+ | 0.06 mm | Austria | $ 22,000 | Quote |
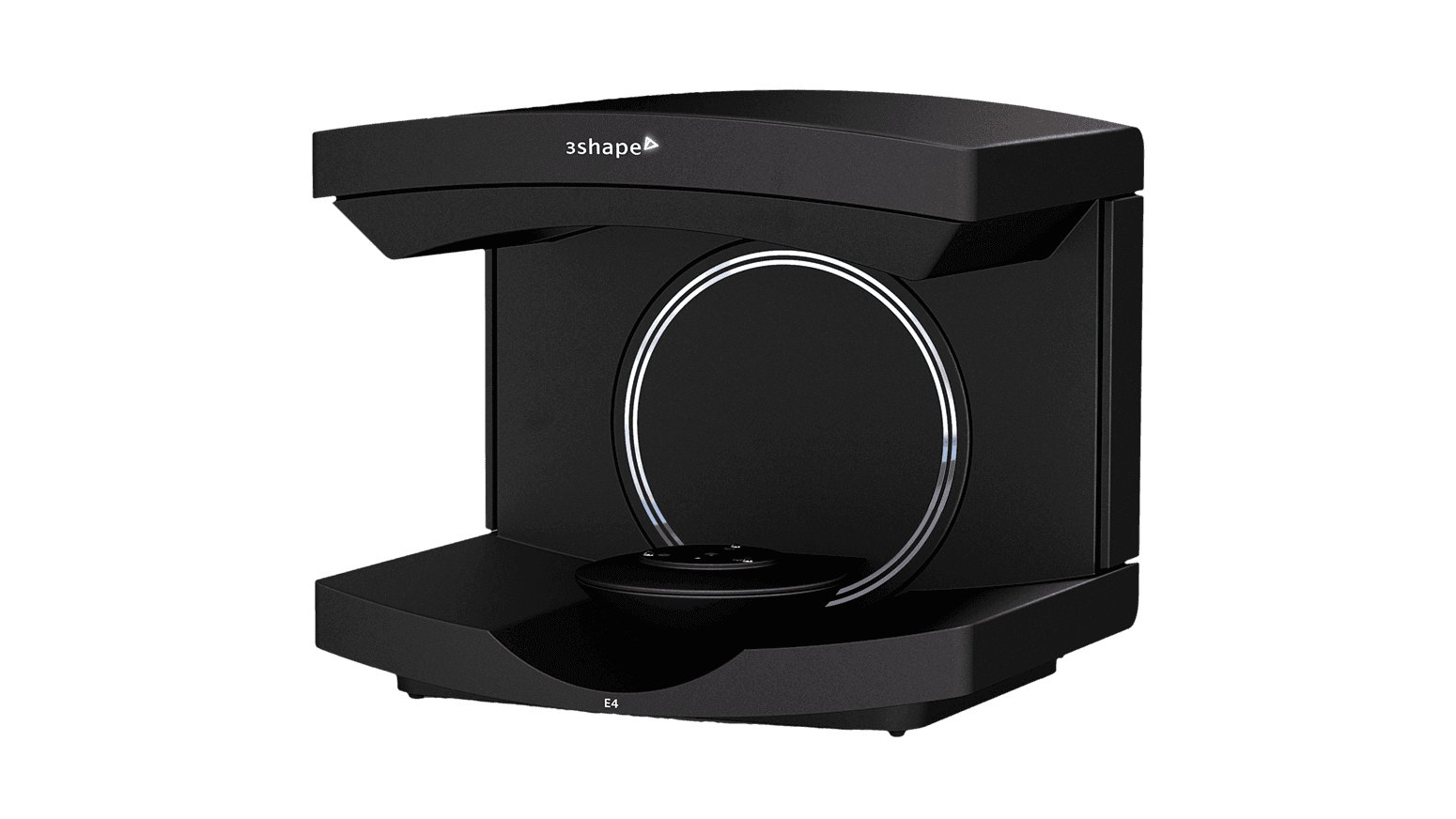
| 3Shape | E4 | 0.04 mm | Denmark | $ 26,000 | Quote |
| Zirkonzahn | S600 ARTI | – | Italy | upon request | Quote |
The products in the table are ranked by price (low to high).

| Brand | Product | Accuracy | Country | Price
Approximate starting prices based on supplier-provided information and public data. Prices may vary by region, over time and do not include additional products or services (taxes, shipping, accessories, training, installation, …).
| |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shining 3D Dental
Product data validated by the manufacturer.
| AutoScan DS-MIX | 0.007 mm | China | $ 9,999 | Get a quote |
| Medit | T500 | 0.07 mm | South Korea | $ 12,000 | Get a quote |
| Dentsply Sirona | inEos X5 | – | United States | $ 15,000 | Get a quote |
| EGSolutions | DScan 3 | – | Italy | $ 15,000 | Get a quote |
| imes-icore | I3Dscan color HR | – | Germany | $ 15,000 | Get a quote |
| CADstar | CS.Neo Pro | – | Austria | $ 19,000 | Get a quote |
| dental wings | 7Series | 0.015 mm | – | $ 20,000 | Get a quote |
| Zfx | Zfx Evolution Plus | – | Germany | $ 20,000 | Get a quote |
| AmannGirrbach | Ceramill Map 200+ | 0.06 mm | Austria | $ 22,000 | Get a quote |
| 3Shape | E4 | 0.04 mm | Denmark | $ 26,000 | Get a quote |
| Zirkonzahn | S600 ARTI | – | Italy | upon request | Get a quote |
Overview of the best dental lab 3D scanners
| Country | Denmark |
| Accuracy | 0.04 mm |
| Price | $ 26,000 |
Scanning a full arch in nine seconds, the 3Shape E4 is the fastest scanner on our shortlist and, with an accuracy of 4 microns, also one of the most accurate.
It uses a blue light projector and can be used in the 3D dental scanning of impressions, models, dies, and more.
Danish company 3Shape has given the E4 an open design and, unusually, a total of four 5-megapixel cameras.
| Country | Austria |
| Accuracy | 0.06 mm |
| Price | $ 22,000 |
The Ceramill Map 200+ from Austrian company AmannGirrbach is an automatic 2-axis white light scanner that offers convenience and accuracy.
It has a compact footprint and high-resolution sensors, while its open interface allows scans to be sent to third-party CAD software.
Billed as an entry-level machine for 3D dental scanning, the Ceramill Map 200+ lacks some of the features of the Map 600, such as automatic model positioning and blue light technology.
| Country | Austria |
| Accuracy | – |
| Price | $ 19,000 |
CADstar’s CS.Neo Pro is a 2-axis white light scanner with 5-micron accuracy and a pair of 2-megapixel cameras.
Features include deep cavity scanning, automatic rescanning, “click-less” workflow, and CAD integration.
CADstar, based in Austria, also markets an entry-level version of the machine, the CS.Neo, with the same accuracy and resolution as the Pro version.
| Country | – |
| Accuracy | 0.02 mm |
| Price | $ 20,000 |
Canadian company dental wings, part of the Straumann Group, is a specialist in digital dental technologies.
The dental wings 7Series, a desktop laser scanner for dental models and impressions, offers three rotational and two linear axes for comprehensive scan coverage, even in deep cavities.
Unlike most desktop scanners, it uses a single laser line instead of structured light, and therefore has an enclosed design.
| Country | United States |
| Accuracy | – |
| Price | $ 15,000 |
The Dentsply Sirona inEos X5 is a blue light scanner for dental applications with a 5-axis robotic arm. At 2.1 microns, it is the most accurate scanner on our shortlist.
Suitable processes include impression scanning, triple tray scanning, texture scanning, and multi-die scanning. The scanner also adapts to different models of articulator and positioning of impressions.
Dentsply Sirona, based in Pennsylvania, also markets dental software and production systems.
| Country | Italy |
| Accuracy | – |
| Price | $ 15,000 |
The 2-axis DScan 3 is a compact dental scanner from Italian company EGSolutions. Using blue light technology, the scanner offers 15-micron accuracy and 1.3-megapixel camera resolution.
The DScan 3 is a standalone unit with built-in computer, requiring no other hardware to operate.
It is an entry-level scanner with fewer features than the company’s more versatile and accurate dental scanning solution, the DScan 4.
| Country | Germany |
| Accuracy | – |
| Price | $ 15,000 |
The I3Dscan Color line of scanners, from German company imes-icore, are built for flexible color dental scanning and offer a fully automated Z-axis in addition to open/closed scanning.
The HR version of the dental desktop scanner provides 2.8-megapixel camera resolution and 4-micron accuracy, compared to the 6-micron accuracy of the non-HR model. Both use blue light technology.
Included adapters enable the scanning of impressions, dies, and other objects.
| Country | South Korea |
| Accuracy | 0.07 mm |
| Price | $ 12,000 |
South Korean company Medit developed the T500 to be one of the fastest blue light dental scanners on the market.
The scanner has a 3-axis arm and can automatically capture both sides of a dental impression for one-step scanning.
Medit launched the current generation of the T-Series line of scanners, which also includes the 2-axis T300, in September 2020.
| Country | China |
| Accuracy | 0.007 mm |
| Price | $ 9,999 |
Shining 3D’s AutoScan DS-MIX is a high-resolution blue light scanner that is particularly suited to high-end implant and veneer applications.
The Chinese company has fitted the scanner with two 5-megapixel cameras, giving it higher-than-ordinary resolution.
The AutoScan DS-MIX is also highly versatile and able to scan impressions, various branded articulators, and other items.
| Country | Germany |
| Accuracy | – |
| Price | $ 20,000 |
German company Zfx developed the Evolution Plus to reduce machine footprint without compromising the quality of dental scanning. The scanner, which uses green LED stripe light projection, has an open design.
Accurate, 9-micron scanning is complemented by features like a straight-to-3D-printer workflow and automatic texture mapping, while the machine can scan up to 12 items at once.
The open design can house articulators from the majority of leading brands.
| Country | Italy |
| Accuracy | – |
| Price | upon request |
The Zirkonzahn S600 ARTI is a structured light scanner with two cameras (plus optional third) and an accuracy of 10 microns.
Suitable for dies, arch segments, full arch models, and more, the S600 ARTI provides features like two-sided scanning, color scanning, and group matching.
Zirkonzahn, based in Italy, also markets production systems, materials, and accessories for the dental industry.
Dental 3D scanner price
The price of dental 3D scanners depends on factors like build quality, number of mechanical axes, light source, and bundled accessories and software.
Prices start at around $10,000 and can go up to over $20,000.
Types of 3D dental scanners
Desktop dental 3D scanners
Desktop dental scanners or dental lab scanners are stationary machines used to scan synthetic items such as dental impressions and models.
Most of these desktop or “benchtop” scanners use structured light technology, in which a series of patterns is projected onto the surface of the dental model and then photographed by one or more cameras to determine the shape of the part.
Some scanners use a laser line instead of structured light, but the principle is similar: the laser line appears bent on surface contours, and sensors detect the lines to determine the shape of the part.
Most desktop dental 3D scanners are capable of scanning dental models such as full arches and dies, and the newest generation of scanners can also capture negative dental impressions.
Since desktop dental scanning does not require any direct contact with a patient, these machines are usually found in dental laboratories (alongside dental production equipment like milling machines) rather than in dental clinics. They are regularly used in the production of dental prostheses.

Intraoral 3D scanners
Intraoral 3D scanners are small portable handheld scanners used to examine the inside of a patient’s mouth during a clinical checkup or prior to a procedure.
Like desktop scanners, intraoral dental scanners use structured light or laser technology, but without the ability to rotate and manipulate the scanned object (here, the patient’s teeth and gums).
Intraoral scanners are used in dental clinics and are sometimes described as a “chairside” solution. Scans captured with an intraoral scanner can be processed almost instantaneously and can be used for several purposes, including prosthodontics and disease prevention.

Which is better?
The simple answer is that intraoral scanners produce very fast results, while dental lab scanners may be more accurate. However, desktop and intraoral scanners are used for different purposes.
To understand how, we need to look at how dental restorations have traditionally been made:
- An impression is taken from the patient.
- The impression is filled with another material to create a positive cast.
- The cast is used to make a second, more durable impression.
- This impression is filled with metal, plastic, or ceramic material to make the prosthesis.
An intraoral dental scanner is a digital alternative to traditional impression taking (step 1), in which a patient’s teeth and gums are submerged in a liquid or soft material to create a negative imprint. By using an intraoral scanner instead, dentists can gather information more quickly and without waiting for materials to dry.
Desktop dental scanners are more like an alternative to casting (Steps 2 and 3). They allow a dentist to turn a traditional impression — sometimes more accurate than an intraoral scan — into a digital model, which can then be used to fabricate a prosthesis, orthodontic device, or physical model.
The digital dentistry CAD/CAM workflow
How it works
The digital dentistry workflow varies depending on the desired outcome. Dentists may want to create dentures, a custom night guard, or simply store their patient’s data on file.
Here is a typical digital workflow for the production of a dental prosthesis such as a crown:
- The dentist takes an impression of a patient’s teeth and gums using an impression tray filled with a liquid or soft material. The impression solidifies.
- The impression is sent to a laboratory.
- a) The impression is scanned using a desktop dental scanner, or
b) The impression is cast to create a positive model. The model is then scanned using a desktop dental scanner. - The technician uses CAD to design a dental prosthesis or other object, using the scan data as a foundation.
- The digital design is sent to a 3D printer, CNC mill, or grinding machine to make a prosthesis or other object.
- The technician sends the prosthesis to the dentist for fitting.

What can be scanned (objects)
Desktop 3D dental scanners can be used to scan different objects, including but not limited to:
- Impressions: Modern 3D scanners can capture negative dental impressions, in spite of the hard-to-reach cavities that represent the inverted teeth.
- Full arch models: Dental models are positive casts made from impressions. Virtually all desktop scanners can capture models of the upper or lower jaw, and some can scan both at once.
- Dies: A die is a positive duplicate of a prepared tooth with a base or “stump”. It is designed to be freely removed and reattached to the full arch.
- Articulators: Articulators are mechanical frames that replicate the motion of the human jaw, and are used to ensure proper occlusion (bite). Several desktop scanners can capture an entire articulator loaded with models of the upper and lower jaws.
- Implants and abutments: Implants are small fixtures that attach to the jawbone or skull in order to support a dental prosthesis like a crown or denture. Abutments are fitted between the implant and crown/denture.
You may also like:
3D printing and 3D scanning for the dental industry
What scans are used for (applications)
Dentists capture 3D scans for different reasons, from prosthesis production to digital archiving:
- Production of prostheses: Using 3D scans of a patient’s mouth, technicians can design dental prostheses like dentures (full sets of replacement teeth), bridges (false teeth implanted between existing teeth or prostheses), and crowns (partial tooth replacements). These can then be fabricated using digital production technologies like CNC milling or grinding.
- Production of aligners: Dental laboratories can use dental 3D scans to create patient-specific corrective devices like dental aligners. Some of the leading producers of clear aligners use 3D printing as a manufacturing method.
- Production of mouth guards: Many traditional mouth guards require the wearer to heat up the rubber guard before biting into it to create a close fit. 3D scanning and 3D printing creates an equally accurate fit while allowing for a wider variety of production materials.
- Surgical planning: Obtaining a comprehensive 3D scan of a patient’s mouth gives surgeons a chance to familiarize themselves with a procedure before surgery. This may involve virtual preparation or the fabrication of physical models.
- Tracking patient progress: 3D scans allow dentists to monitor changes in a patient’s oral health and tooth movement over time.
- Digital archiving of patient data: 3D scans can be saved indefinitely and require no physical space, allowing dentists and technicians to keep patient data on file for future use.
Benefits of 3D scanning for dental labs
3D scanning can benefit dental labs in many ways.
One of the most important benefits is speed. 3D scans take less than a minute — sometimes much less — and can be transferred without relying on physical mail services. For instance, Medit has calculated that the busiest labs could save up to 450 hours per year.
Another advantage is potential cost savings. Although a 3D dental scanner may seem expensive, they offer excellent ROI, especially for busier labs, since they reduce manual workload and enable a greater number of cases to be processed.
Lab 3D scanners also provide a high degree of accuracy. Traditional techniques can involve multiple stages of casting, and materials are liable to shrink, expand, or deform with each new duplication. Once a scan has been obtained, its measurements are stable.
What to look for in a dental lab 3D scanner?
| Feature | Range | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Structured light (blue, white) or laser | Most desktop dental 3D scanners use structured light technology, with blue light now generally favored over white light. Laser line technology works in a similar way but may be slower. |
| Degrees of freedom | ~2–5 | A scanner’s listed number of axes or DoF usually indicates mechanical axes of the arm but may also include projector/camera movement. The number of mechanical axes is the more significant feature. |
| Accuracy | ~4–15 μm (microns) | Dental 3D scanner accuracy is measured in microns or micrometers. Machines with ISO 12836 certification have used standardized testing to establish their level of accuracy. |
| Resolution | Up to ~5 MP (megapixels) | Camera resolution, measured in megapixels, may affect the clarity of 3D scans but is less important than accuracy. |
| Color / texture | Yes or no | Some dental scanners offer texture scanning and/or color scanning, which may be useful for tooth shade matching or capturing handwritten notes on models. |
| Speed | 9 seconds to >1 minute for full arch scan | Most 3D scanners list their speed as the time it takes to scan a full arch model. However, this may not be a reliable indicator of productivity, since software processing times may be longer than scanning times. |
| Scan volume | Up to ~140 x 140 x 140 mm | Since most dental 3D scanners are designed to process similar items, scan volume does not vary greatly. Scanners that can hold large items like dental articulators usually specify this capability. |
| Machine design | Open or closed | Scanners may or may not be enclosed with a door. Open designs may give more flexibility, while closed designs are essential for laser scanning, where darkness is required. |
| Multi-item scanning | Number of dies, “all-in-one” | Dental 3D scanning often involves scanning several items at once, such as a pair of arches or set of dies. |
| Articulator scanning | Static or dynamic | Desktop scanners that offer articulator scanning may provide dynamic scanning, which enables the scanner to capture natural bite movement. Some manufacturers provide jigs to fit specific articulator brands and models. |
| Software | Open or proprietary | Some scanners only work with bundled proprietary software while others work with third-party software like exocad. Labs already familiar with a third-party suite may prefer the latter. |
| Output format | STL, PLY, OBJ, proprietary | Most scanners and software packages allow users to export files in standard formats for 3D printing, milling, etc. |
| Company age | – | A company’s age, size, and reputation is not necessarily a guarantee of quality, but it may be a good indicator of long-term customer support and warranty fulfillment. |
Dental scan software
Dental imaging software is usually included with the 3D scanner and allows technicians to control scan operation. Popular dental scanning software suites include exocad exoscan, Medit Collab, and Zirkonzhan.Scan.

Functions of scanning software include workflow management, parameter selection, and automatic or manual target identification. Many applications provide preset scanning strategies for different targets like impressions and dies.
Scanning software creates a point cloud and turns it into a mesh that can be read by CAD/CAM software.
Although the two are often integrated, scanning software should not be confused with dental CAD software, which is used to design dental restorations like crowns, bridges, and veneers, as well as retainers and other items. CAD software like exocad DentalCAD, Ceramill Mind, and Zfx DentalCAD do not control the operation of the scanner hardware.
Some software suites contain both scanning and CAD applications, such as dental wings DWOS, 3Shape Dental System, and Dentsply Sirona inLab.

CAM modules (often integrated as modules into CAD software) export data into a file that can be read by the milling machine or dental 3D printer.
FAQ
Most dental 3D scanners use structured light scanning technology, projecting lines of light onto the scanned object and measuring the deformation of those lines.
Dental 3D scanners capture point clouds, which are turned into digital 3D files called meshes. After adjustment with CAD software, these meshes can be 3D printed, to create models or clear dental aligners, for example.
Laboratory dental scanners are built to scan dental impressions (negative imprints of teeth and gums) and dental models. However, intraoral dental scanners can scan directly inside a patient’s mouth.
In many situations, dental 3D scanning can greatly improve lab productivity and provide a good return on investment.
 English
English  Français
Français