The 13 best construction 3D printers in 2024

What are the best house 3D printers?
A construction 3D printer is a machine that can build houses by depositing a material (concrete for example) layer by layer. Concrete 3D printing – a.k.a. “Construction 4.0” – is a similar 3D printing technology to the one that FFF 3D printers use. Paste-type material, in this case, concrete or earth materials, is pushed through a nozzle in layers to print buildings in 3D.
Concrete 3D printing in the construction industry helps save time, effort, and material compared to traditional construction methods. It’s important to note, though, that 3D printers are not yet capable of creating a fully functional house.
Only the frame and walls of the house are built; other elements, such as windows, electricity, or plumbing, need to be installed separately. But concrete 3D printers can also be used to print bridges, benches, or simply outdoor decorations.
To provide a complete overview of the construction 3D printer market, we have listed 12 house 3D printing solutions. Some of them are 3D printers available for sale, while some are still at the start-up prototype stage or are external construction 3D printing services.
13 house construction 3D printers
| House 3D printer | Category* | Type** | Build size (m) | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BetAbram P1 | Available | Gantry system | 16 x 8.2 x 2.5 | Slovenia |
| COBOD BOD2 | Available | Gantry system | 14.62 x 50.52 x 8.14 | Denmark |
| MAXI PRINTER | Available | Robotic arm | 12.25 x 12.25 x 7 | France |
| CyBe Construction CyBe RC 3Dp | Available | Robotic arm | 2.75 x 2.75 x 2.75 | Netherlands |
| ICON Vulcan II | Available | Gantry system | 2.6 x 8.5 x ∞ | United States |
| MudBots 3D Concrete Printer | Available | Gantry system | 1.83 x 1.83 x 1.22 | United States |
| Total Kustom StroyBot 6.2 | Available | Gantry system | 10 x 15 x 6 | United States |
| WASP Crane WASP | Available | Delta system | Ø 6.3 x 3 | Italy |
| Apis Cor | Project | Robotic arm | 8.5 x 1.6 x 1.5 | Russia |
| Batiprint3D 3D printer | Project | Robotic arm | Up to 7m high | France |
| SQ4D – ARCS | Service | Gantry system | 9.1 x 4.4 x ∞ | United States |
| Contour Crafting | Service | Gantry system | – | United States |
| XtreeE | Service | Robotic arm | – | France |
Build volumes are indicative and may vary based on the specific configuration of the machine.
*Category: some 3D printers are available for sale, others are working projects, and some are only available via a rental service.
**Type: construction 3D printers either use a gantry system (like oversized desktop 3D printers with X, Y, and Z axes) or a mechanical, robotic arm.
How to build 3D printed houses?
Here we explain how 3D printers are able to print houses with paste extrusion.
House 3D printing technology
House 3D printers use extrusion technology. Some construction 3D printers look like super-sized desktop FFF/FDM 3D printers (gantry style), whereas others consist of a rotating mechanical arm.
In both cases, paste-type components such as concrete are used as filament. The material is pushed out of a special nozzle to form layers. To put it (very) simply, paste extrusion is similar to using a piping bag to spread frosting on a cake.
The printer creates the foundations and walls of the house or building, layer by layer. The ground is literally the printer’s build plate. Some concrete 3D printers, however, are used to 3D print brick molds. When molded, the bricks are then piled atop each other manually (or with a robotic arm).
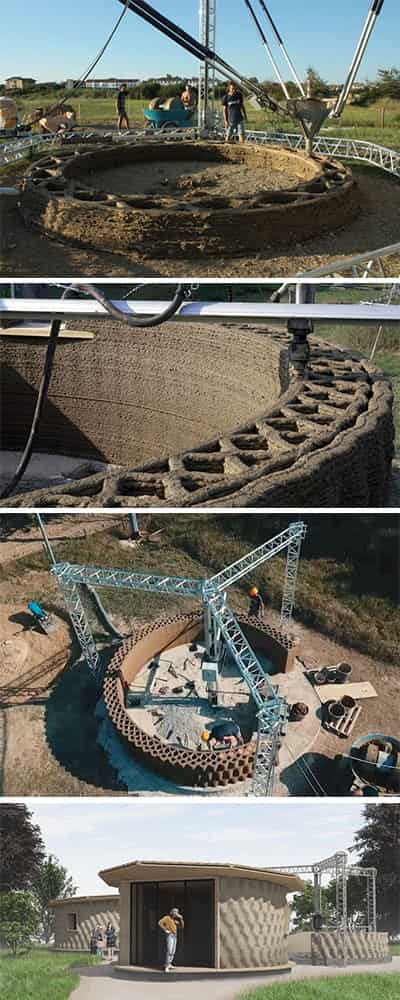

Benefits of house 3D printing
Eco-friendly
3D printed houses can be built with organic, eco-friendly materials. Moreover, some house 3D printers use solar energy and generate low CO2 emissions.
Affordable
House 3D printers can build affordable housing, being of great aid for people in poverty-stricken regions or after natural disasters.
Scalable
Construction 3D printing reduces certain building costs. For example, the cost for 1 square meter of a wall using traditional construction methods is approximately $75, whereas with the Apis Cor house 3D printer it is only $27.
Efficient
Since the materials are 3D printed on-demand, the machines produce less waste. Also, construction 3D printers can finish a home’s foundations in less than a few days, while traditional construction methods take several weeks or even months.
Design flexibility
With a 3D construction printer, it’s possible to easily create curved walls and unique facades. (Good thing it’s possible to 3D print furniture to match the curves!)
Limits of 3D printing houses
Expensive initial investment
House 3D printers can sometimes cost up to one million dollars.
Partially-built houses
House 3D printers only build house frames. The 3D printing process is usually paused to manually settle plumbing, wiring, and rebars.
Rough exterior
Most 3D printed homes’ exteriors are not as smooth as traditionally-built houses.
Lack of certification
Construction sites are regulated by laws and there are important safety standards that need to be met, which can be challenging with 3D printing techniques (varying repeatability, dimensional stability, etc.).
Another downside that has been noted over the years is that house 3D printing can potentially harm local economies, especially in poverty-stricken regions or cities with high unemployment rates. Indeed, since construction 3D printers reduce the need for manual labor, they create much less employment for local workers.
Differences between 3D printed houses and traditional houses
Concrete 3D printing saves time, uses less material, and requires less manual labor. Even 3D printed houses have a rougher exterior, post-processing is an option just as it is for regular 3D printed objects. 3D printed houses tend to be smaller due to 3D printer build volume limits, but this is not always the case.
Construction 3D printers: overview
We break down construction 3D printers into three categories: house 3D printers that are available for sale, concrete printer prototypes, and 3D concrete printing services.
House 3D printers available for sale
BetAbram is a small Slovenian team that has been working on construction 3D printing hardware since 2012. Their flagship home 3D printer, the BetAbram P1, is currently in its second version and is available with optional print heads: basic, “Orto” for smoother layers, and rotating for more design possibilities.
This construction 3D printer is fast, reaching announced speeds of up to 60 meters per minute. The BOD2 is modular and can be adapted is many different sizes. COBOD is a 3D Printhuset company.
Constructions-3D is a subsidiary of French 3D printer retailer Machines-3D.
Their MAXI PRINTER machine is mobile thanks to its caterpillar-style rubber tracks and fits into a 20-foot shipping container for easy transport from one construction site to another.
The CyBe RC 3Dp consists of a single robotic arm with a nozzle at its end.
This easy-to-move house 3D printer is capable of reaching up to 2.75 meters high and requires only two people to operate it.
ICON wishes to revolutionize the construction field with their Vulcan II printer. The whole process is designed to be user-friendly with a tablet-based interface, and ICON’s Lavacrete concrete mix is optimized to be easier to print.
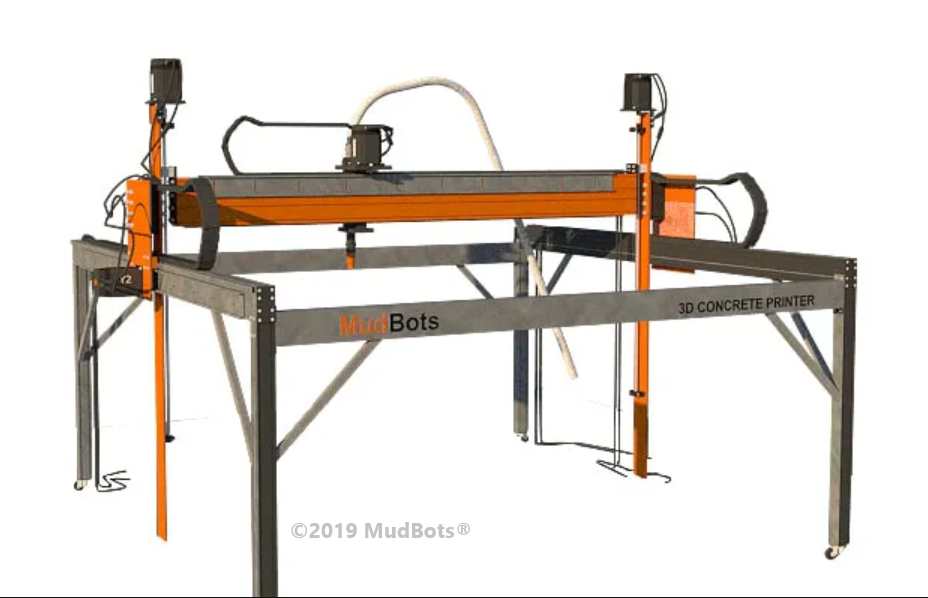
MudBots is a concrete 3D printer manufacturer based in the United States. Their smallest model (1830 x 1830 x 1220 mm approx.) is available at the price of $35,000. Larger build sizes are available as well, reaching up to 30 meters long.
According to MudBots, their 3D printers can 3D print a small house in only 12 hours and can drive costs down 70% compared to traditional construction methods.
StroyBot 6.2
| Country | United States |
| Build envelope | 1000 x 1500 x 600 mm |
| Material | Concrete |
The StroyBot, also known as the Rudenko 3D construction printer (made by Andrey Rudenko), is an all-in-one mobile construction printing system delivered as a kit to be assembled by the user. On average, it is able to print a 100-square-meter house in 48 hours (walls only).
Crane WASP “Infinity 3D Printer”
| Country | Italy |
| Build envelope | Ø 6300 x 300 mm |
| Material | Concrete/Earth materials |
The Crane WASP is the evolution of WASP’s previous construction printer, the BigDeltaWASP 12MT. This open source construction printer is modular and multiple Crane printers can work together on one project, for theoretically infinite 3D printing possibilities.
Concrete printer working projects
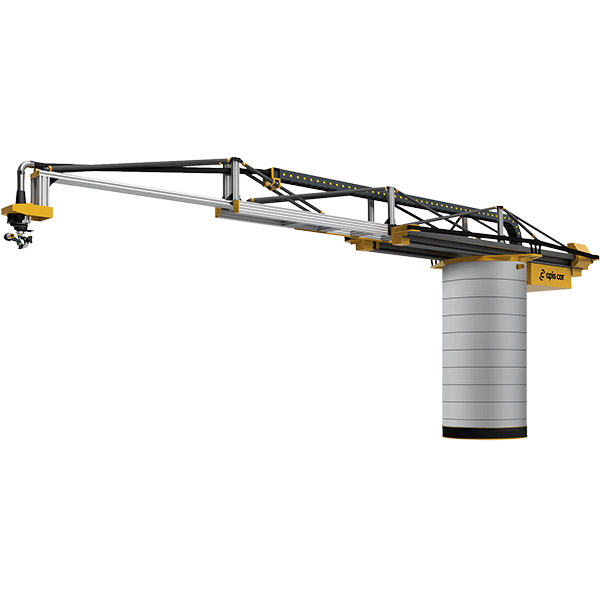
Apis Cor, a 3D construction company, is based in San Francisco and claims to be able to 3D print a house in under 24 hours. Their Apis Cor printer is similar to a robotic arm and has won first place in NASA’s Phase 3 3D-Printed Habitat Competition.
Batiprint3D 3D printer
| Country | France |
| Build envelope | – |
| Material | Concrete/other |
Batiprint 3D made international headlines when completing their Yhnova 3D printed house in Nantes, France. Their 3D printer not only prints cement but also insulation foam, which makes it one of the most complete 3D construction solutions.
Construction printing services
3D printing system
| Country | United States |
| Build envelope | – |
| Material | Concrete |
This automated construction system is able to 3D print large buildings and tall infrastructures. Contour Crafting (a.k.a. CC Corp) aims to make disaster relief more efficient with their concrete additive manufacturing technology.
ARCS
| Country | United States |
| Build envelope | 9100 x 4400 x ∞ mm |
| Material | Concrete |
3D printer
| Country | France |
| Build envelope | – |
| Material | Concrete |
Special mentions: interesting 3D construction projects
DFAB HOUSE

This unique building was completed by a consortium of companies in early 2019 and is based in Switzerland. The 3-story DFAB building offers 200 square meters of space.
Branch Technology C-FAB and WATG’s Curve Appeal design

The WATG architectural design firm won the Branch Technology Freeform Home Design Challenge in 2016. In 2019, their project is set to be printed in Tennessee by Branch Technology’s C-FAB freeform construction 3D printing method.
DUS Architects XL 3D printer (KamerMaker)

The XL 3D printer was created by DUS Architects to build a prototype canal-house (simply dubbed “3D Print Canal House”) in Amsterdam using recycled materials.
Haus.me
This US-based company, previously known as PassivDom (dom.ai), 3D prints walls, floors, and roofs for their fully autonomous prefab houses.

Autodesk metal construction printer
Autodesk may or may not be working on a construction 3D printer that uses metal material. This 3D printer, which is more a pair of robotic arms than a printer, is able to make metal components for construction sites. We can’t wait to hear more about this!

CONCR3DE Armadillo stone 3D printer
CONCR3DE is a Dutch company that manufactures stone 3D printers. They are able to 3D print stone thanks to a special binder jetting process. Their two 3D printers, Armadillo Black and Armadillo White, aren’t able to print a house but can 3D print stone decorations or molds.

Discontinued projects and printers
Many startups have come and gone in the construction 3D printing industry.
D-Shape construction 3D printer
The D-Shape 3D printer is a multifunctional construction 3D printer that can 3D print very large objects, including houses and prototypes. D-Shape seems to be inactive since 2015.
Winsun house 3D printer
The Winsun 3D printer is a house 3D printer that was in the spotlight a few years ago. In 2015, however, Contour Crafting’s CEO accused Winsun of stealing their patented technology. Winsun’s website has since been taken down.
Cazza X1 3D printer
Cazza was founded in 2016 with its X1 construction 3D printer. However, it seems that one of the co-founders stole the company’s funding in 2018, and Cazza is now on standby.
HuaShang Tengda
HuaShang Tengda 3D printed a house capable of withstanding a base 8 earthquake on the Richter magnitude scale. Today, the company seems to be off the radar.
3D printed house time and cost
Construction 3D printing is faster and more affordable than traditional construction methods.
However, since construction 3D printing is still in its early years, it is difficult to provide definitive statements about how long it takes to 3D print a house and how much it costs to 3D print a house.
How long does it take to 3D print a house?
Various construction 3D printer manufacturers such as Apis Cor or ICON boast that they are able to 3D print a small house in 24 hours. As mentioned before though, print jobs generally only include laying down the house’s foundations and walls.
This does save whatever amount of time it usually takes for a standard team to build walls for a certain project. The rest of the timeframe for building a house remains equal.
3D printed house price
In general, it is estimated that a 3D printed house costs 30% to 55% less than a traditionally-built house.
For reference, Apis Cor’s small house cost less than $10,000 to produce, and ICON’s compact 3D printed home even cost less than $4,000.
Construction 3D printer price
A construction 3D printer can cost anywhere between around $180K to over $1M. Robotic arm systems tend to have higher price tags than gantry-type systems.
Other 3D printed infrastructures
Aside from housing or buildings, construction 3D printers are able to 3D print bridges and space-station infrastructures.
3D printed bridges
Construction 3D printers can also 3D print bridges. In 2015, the world’s first 3D printed steel bridge was 3D printed for testing in Amsterdam by MX3D. MX3D printed the final version of their stainless steel bridge in 2018 and installed it in Summer 2021.
In 2017, a 12-meter-long pedestrian bridge was 3D printed in Madrid, Spain. In the same year, the first 3D printed concrete bridge was built in the village of Gemert in the Netherlands.
More recently, in 2019, Shanghai became home to the world’s longest concrete 3D printed bridge. It is 26.3-meters long and 2.6-meters wide, and was 3D printed in only 18 days.
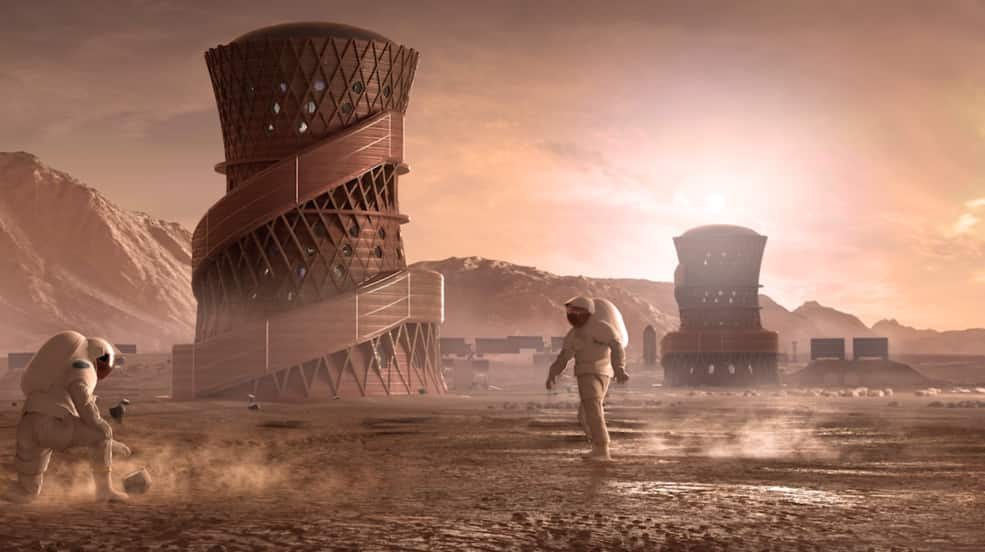
3D printed infrastructures in space
NASA’s 3D-Printed Habitat Challenge has given life to a number of teams dedicated to bringing 3D printing to space. Apis Cor, namely, won the top prize for one of this project’s phases. The goal is to create sustainable and efficient 3D printed housing for deep space exploration.
Many other companies have been involved in space-building projects, including the European Space Agency and Elon Musk’s SpaceX. It is possible that we will see the first space house 3D printers in space sometime in the next couple of decades (!).

FAQ: construction 3D printing
A 3D printed house is a house composed of 3D printed elements, such as 3D printed walls, floors, or roofs. It is also possible to use the term “3D-printed home”.
It can cost as low as $4,000 to 3D print a home. Prices vary greatly according to the material being used and the size of the home to be 3D printed.
See our selection of the best 3D printed house companies here.
There are 3D printed houses for sale in the US (Los Angeles, San Francisco), China, France, Russia, UAE, and many other countries.
No, concrete 3D printing is also for infrastructures such as bridges.
 English
English  Français
Français








