Metal 3D printers in 2024: a comprehensive guide

What is the best metal 3D printer in 2024?
Over the past few years, there has been a surge in both supply and demand for metal 3D printers.
Manufacturers are launching metal additive manufacturing machines that are faster, easier to use, and more powerful with an increasing number of compatible metals.
Many businesses are adopting these 3D metal printing technologies to produce cost-effective metal parts and prototypes, benefiting as well from increased freedom of design linked to additive manufacturing. They are suitable for a variety of industries such as aerospace, automotive, health, engineering, and more.
Although metal 3D printer prices have been slowly and slightly decreasing, these machines are still relatively expensive acquisitions, mostly ranging from $80K to almost $1M.
With our metal 3D printer selection, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of what’s available from well-established and distributed brands, at various price points, and with different metal 3D printing technologies.
The best metal 3D printers in 2024
| Brand | Product | Build size | Country | Price
Approximate starting prices based on supplier-provided information and public data. Prices may vary by region, over time and do not include additional products or services (taxes, shipping, accessories, training, installation, …).
| |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Markforged
Product data validated by the manufacturer.
| Metal X (Gen 2) | 300 × 220 × 180 mm | United States | $ 99,500 | Quote |
| Pollen AM
Product data validated by the manufacturer.
| Pam Series MC | ⌀ 300 x 300 mm | France | $ 140,000 | Quote |
| TRUMPF | TruPrint 1000 | 100 × 100 × 100 mm | Germany | $ 170,000 | Quote |
| EOS
Product data validated by the manufacturer.
| EOS M 100 | 100 × 100 × 95 mm | Germany | $ 350,000 | Quote |
| XJet | Carmel 700M | 501 × 140 × 200 mm | Israel | $ 599,000 | Quote |
| 3D Systems
Product data validated by the manufacturer.
| DMP Flex 100 | 100 × 100 × 90 mm | United States | upon request | Quote |
| Desktop Metal | Production System P-1 | 200 × 100 × 40 mm | United States | upon request | Quote |
| Desktop Metal | Studio 2 | 300 × 200 × 200 mm | United States | upon request | Quote |
| Digital Metal | DM P2500 | 203 × 180 × 69 mm | Sweden | upon request | Quote |
| Formalloy | L-Series | 1000 × 1000 × 1000 mm | United States | upon request | Quote |
| GE Additive | Arcam EBM Spectra L | ⌀ 350 x 430 mm | United States | upon request | Quote |
| GE Additive | M2 Series 5 | 250 × 250 × 350 mm | – | upon request | Quote |
| Renishaw | RenAM 500E | 245 × 245 × 335 mm | – | upon request | Quote |
| SLM Solutions
Product data validated by the manufacturer.
| SLM 125 | 125 × 125 × 75 mm | Germany | upon request | Quote |
| SPEE3D
Product data validated by the manufacturer.
| LIGHTSPEE3D | 300 × 300 × 300 mm | Australia | upon request | Quote |
| TRIDITIVE | AMCELL | ⌀ 300 x 350 mm | Spain | upon request | Quote |
| Velo3D | Sapphire | ⌀ 315 x 1000 mm | – | upon request | Quote |
| Xact Metal
Product data validated by the manufacturer.
| XM200C | 127 × 127 × 127 mm | United States | upon request | Quote |
Technology: The technologies listed above are main categories of metal 3D printing technologies. Most manufacturers have their own branded technologies, which fall into the main categories that are listed in the table.
The products in the table are ranked by price (low to high).

| Brand | Product | Technology | Build size | Country | Price
Approximate starting prices based on supplier-provided information and public data. Prices may vary by region, over time and do not include additional products or services (taxes, shipping, accessories, training, installation, …).
| |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Markforged
Product data validated by the manufacturer.
| Metal X (Gen 2) | FFF | 300 × 220 × 180 mm | United States | $ 99,500 | Get a quote |
| Pollen AM
Product data validated by the manufacturer.
| Pam Series MC | Material Extrusion | ⌀ 300 x 300 mm | France | $ 140,000 | Get a quote |
| TRUMPF | TruPrint 1000 | Laser beam PBF | 100 × 100 × 100 mm | Germany | $ 170,000 | Get a quote |
| EOS
Product data validated by the manufacturer.
| EOS M 100 | DMLM | 100 × 100 × 95 mm | Germany | $ 350,000 | Get a quote |
| XJet | Carmel 700M | NPJ | 501 × 140 × 200 mm | Israel | $ 599,000 | Get a quote |
| 3D Systems
Product data validated by the manufacturer.
| DMP Flex 100 | DMP | 100 × 100 × 90 mm | United States | upon request | Get a quote |
| Desktop Metal | Production System P-1 | Binder jetting (multi-step) | 200 × 100 × 40 mm | United States | upon request | Get a quote |
| Desktop Metal | Studio 2 | BMD | 300 × 200 × 200 mm | United States | upon request | Get a quote |
| Digital Metal | DM P2500 | Binder jetting (multi-step) | 203 × 180 × 69 mm | Sweden | upon request | Get a quote |
| Formalloy | L-Series | Laser beam DED | 1000 × 1000 × 1000 mm | United States | upon request | Get a quote |
| GE Additive | Arcam EBM Spectra L | EBM | ⌀ 350 x 430 mm | United States | upon request | Get a quote |
| GE Additive | M2 Series 5 | Laser beam PBF | 250 × 250 × 350 mm | – | upon request | Get a quote |
| Renishaw | RenAM 500E | Laser beam PBF | 245 × 245 × 335 mm | – | upon request | Get a quote |
| SLM Solutions
Product data validated by the manufacturer.
| SLM 125 | Laser beam PBF | 125 × 125 × 75 mm | Germany | upon request | Get a quote |
| SPEE3D
Product data validated by the manufacturer.
| LIGHTSPEE3D | CSAM | 300 × 300 × 300 mm | Australia | upon request | Get a quote |
| TRIDITIVE | AMCELL | FFF | ⌀ 300 x 350 mm | Spain | upon request | Get a quote |
| Velo3D | Sapphire | Laser beam PBF | ⌀ 315 x 1000 mm | – | upon request | Get a quote |
| Xact Metal
Product data validated by the manufacturer.
| XM200C | Laser beam PBF | 127 × 127 × 127 mm | United States | upon request | Get a quote |
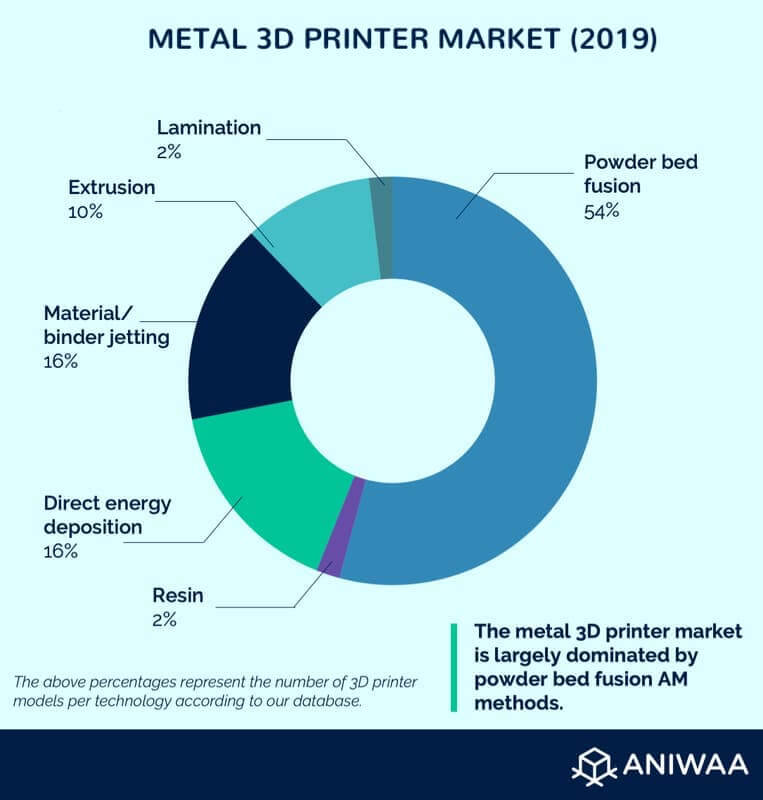
Main types of metal 3D printing technologies
The four main types of 3D metal printing technologies are:
- Metal Powder Bed Fusion 3D printing (SLS, SLM, DMP)
- Directed Energy Deposition (DED)
- Metal filament extrusion (FFF, FDM)
- Material Jetting and Binder Jetting
There are also some resin-based metal 3D printers, and metal sheet lamination 3D printers, but they are harder to come by.
It is not uncommon to see different acronyms and names for similar technologies. Each brand markets their own, proprietary methods. Some metal 3D printer companies even use a mix of different technologies.
Here we provide a deeper look into each 3D metal printer from our list. They are grouped together according to their main 3D printing technology type (powder bed fusion, material/binder jetting, extrusion, and DED).
Extrusion-based metal 3D printer selection (FFF, FDM)
Extrusion consists of heating the material (filament) and pushing it through a nozzle. In the metal 3D printing case, the filament is generally made up of metal particles mixed into a binding agent.
After the part is 3D printed, the result is a raw object or part; it must go through several post-processing steps– such as debinding and sintering– to attain its final form.

Desktop Metal’s Studio is an office-friendly, end-to-end metal 3D printing system. Aside from the printer, the Studio line also includes a debinding machine and a furnace for sintering. Indeed, parts 3D printed with this Desktop Metal 3D printer are “green”.
The Studio printer, with its proprietary Bound Metal Deposition technology, uses filament that is filled with small, metal rods. During debinding, the binding material (wax and polymer binders) is dissolved thanks to a proprietary liquid substance. The part is left porous, and must go in the furnace for its particles to fuse and densify the part.
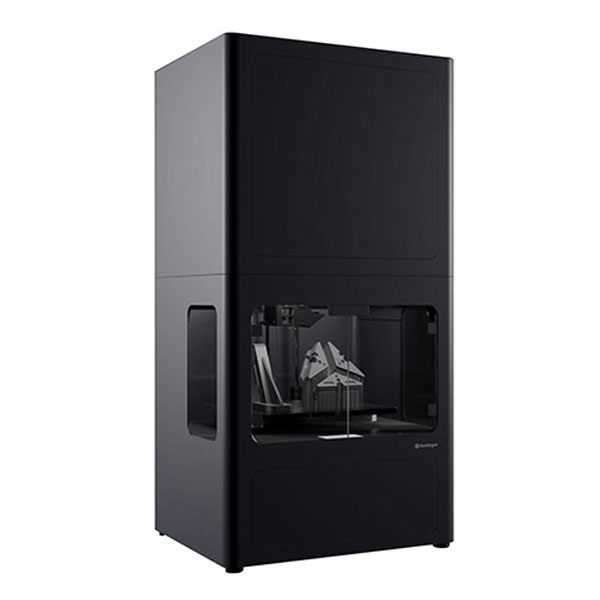
MarkForged is specialized in continuous fiber 3D printing, but also offers metal 3D printing with their Metal X system, featuring Atomic Diffusion Additive Manufacturing (ADAM) technology.
This MarkForged 3D printer extrudes metal-filled plastic filament to form the part, which must then be washed with a special debinding fluid (Wash-1 Station) and then sintered in a furnace (Sinter-1 or Sinter-2 MarkForged machines).
Available metal 3D printer filament includes various Steels (H13, A2, D2 tool steels, 316L stainless steel) as well as Inconel, Copper, and Titanium.
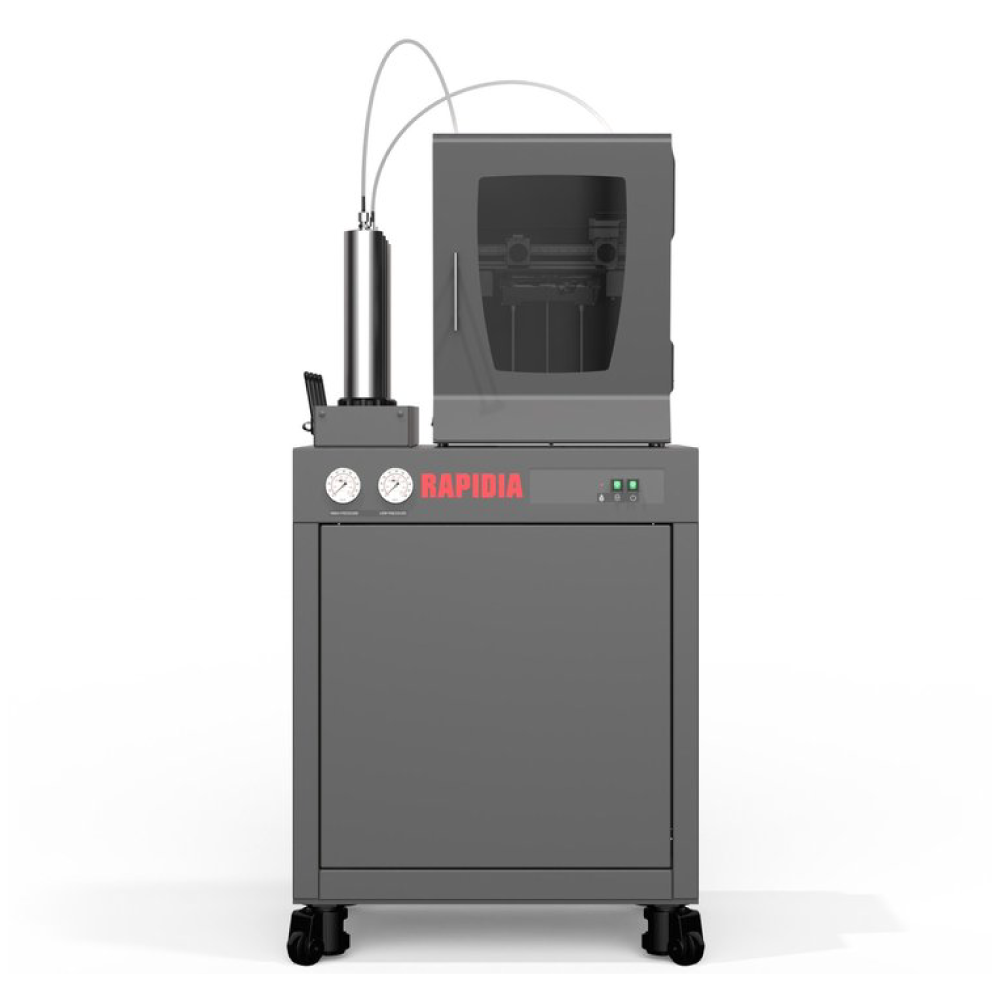
Canada-based Rapidia offers an interesting and unique way to 3D print metal. They use a water-based metal paste, which eliminates the need for chemical debinding. The water evaporates during the 3D printing process, so the part only needs to go through the furnace in order to completely solidify and attain its final form.
Confirmed, available paste types include several Stainless Steels, Inconel, and a few ceramics. Copper, Tungsten Chrome Carbide, Titanium, and various other metals are in development.
The ExOne Metal Designlab, designed in collaboration with Rapidia, works on the same basis.
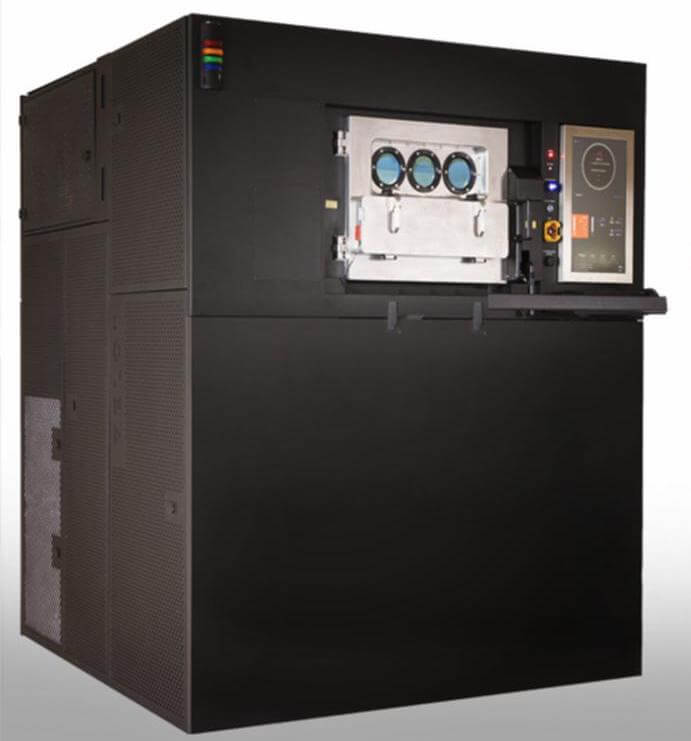
Pollen AM is a French manufacturer that has been producing pellet 3D printers since 2013. Their Pam Series MC is a delta-style 3D printer (cylindrical build volume) that can print metals, ceramics, and thermoplastics.
It extrudes injection-molding-grade pellets instead of metal 3D printer filament, driving material costs down significantly. Pollen AM names their technology “Pellet Additive Manufacturing”.
This machine was built with one goal: enable mass production 3D printing of metal parts 24/7. The AMCELL is fully automated, with auto feedstock control, environment control (temperatures, humidity, air filtering), and an ejection system fitted with a conveyor belt.
Rather than providing one, big build volume, the TRIDITIVE AMCELL boasts eight delta-style ø 220 x 330 mm build areas. Its eight “robots” deposit metal-infused filament to create 3D metal parts. TRIDITIVE states that resulting parts are similar to ones produced with traditional MIM (Metal Injection Molding) methods.
TRIDITIVE’s technology is called Automated Multimaterial Deposition®.
Metal powder bed fusion 3D printer selection (SLS, SLM, DMP, and more)
At the moment, the most commonly used metal additive manufacturing technology is powder bed fusion 3D printing. Simply put, the 3D printer creates objects out of a bed of powdered metal by using a powerful laser.
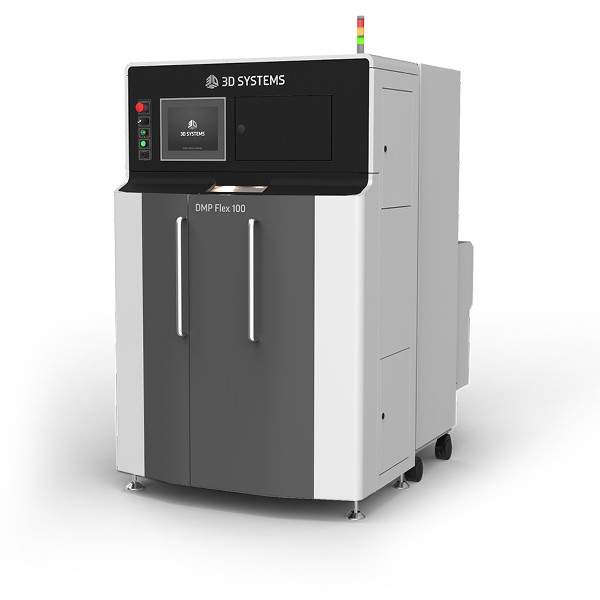
3D Systems, a historical actor on many 3D printing fronts, presents the DMP FLEX 100 as a fast, precise, and affordable metal 3D printer. It offers impressive part repeatability and surface finishes, of around 20 μm and 5 Ra μm respectively. DMP stands for Direct Metal Printing.
The printer comes with 3D Systems’ software 3DXpert All-in-One Software Solution for Metal Additive manufacturing. Their LaserForm metal 3D powders are certified.
This compact metal 3D printer is destined for the production of small parts in small quantities. Its material portfolio is especially interesting for medical use cases, namely dental crowns and bridges. EOS certified metal powders include Cobalt-Chrome, Stainless Steel, and Titanium.
The EOS M100’s laser spot is precise enough to provide a great level of detail, backed by 200 W of powder.
Originally a Swedish company, Arcam was acquired by GE Additive a few years ago. The Arcam EBM Spectra L is up to 20% faster than its predecessors and is able to reduce part costs by around 10%.
This metal 3D printer is dedicated to Titanium 3D printing, but Copper is in the pipeline as well. Its laser beam power is equal to 4.5 kW, partly explaining the printer’s high melting capacity and productivity. Common applications for this printer include orthopedic implants and parts for the aerospace industry.
Concept Laser is the company behind GE Additive’s M2 Series 5. It offers an easy, optimized workflow, with a separate processing chamber and handling area that is integrated into the system. This closed-loop material system ensures a safe environment that is free of powder for the operator.
The M2 metal additive manufacturing solution is compatible with a range of metals, from Stainless Steels to Aluminum, Nickel, Titanium, and Cobalt-Chrome.
The RenAM 500E is Renishaw’s entry-level metal additive manufacturing solution. It offers a relatively large build volume and powder can be handled via a dedicated glove box to avoid powder from getting free.
This system is also equipped with an oxygen sensor and a proprietary emission-filtering system branded SafeChange™.
Officially established in 2006, SLM Solutions has been a historical player in the powder bed fusion industry for many years. The SLM 125 boasts an open software architecture that allows users to tweak the system’s parameters according to specific use cases, materials, and general needs.
Options such as laser monitoring and melt pool monitoring are available for businesses that require full transparency and control over their production series.
The TruPrint 1000 is TRUMPF’s most compact metal 3D printing system, with a 100mm-tall cylindrical build volume. It is suitable for the production of small parts and prototypes, and even small production series when equipped with the multilaser option that increases the printer’s speed.
This metal 3D printer can be operated remotely via a tablet application, which also gives access to its onboard camera stream.
The Velo3D Sapphire is a high-volume metal 3D printer from the US designed for production series. This metal 3D printer features Velo3D’s Intelligent Fusion technology to allow for complex geometries and 0° overhangs.
The system is also equipped with a range of metrology sensors that measure each and every layer that is 3D printed.
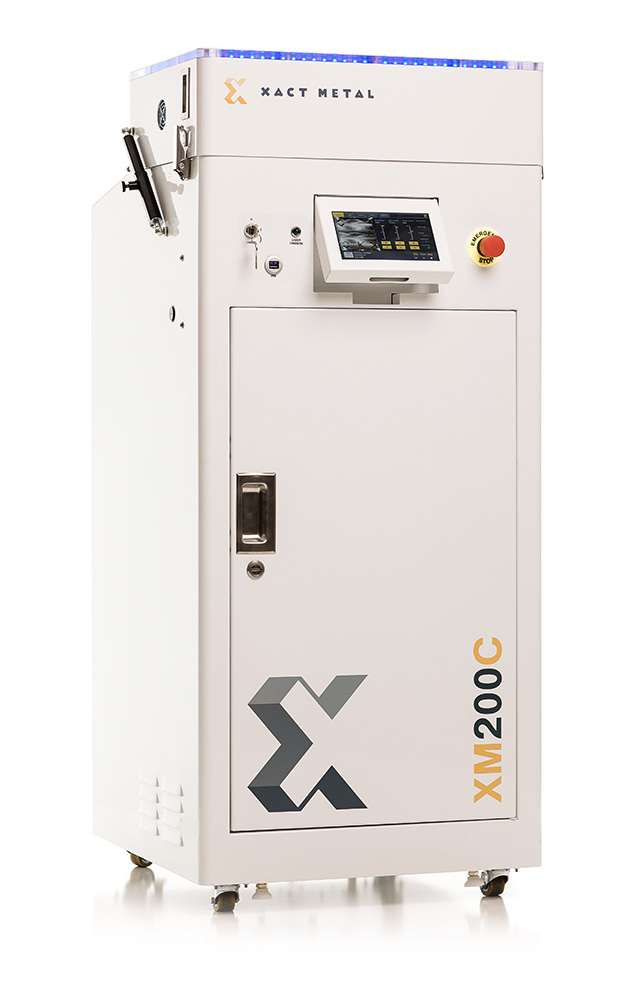
The XM200C is Xact Metal’s entry-level metal 3D printing solution. It is suitable for both research purposes and small production series. The XM200C benefits from a proprietary Xact Core gantry system for precise movements with a fusing speed of up to 500 mm/s.
Xact Metal offers their own materials, branded Xact Powder, including various Stainless Steels, Super Alloys, Tooling Steels, Aluminum, Titanium, Bronze, and Copper. Advanced users are able to use their own metal powders if needed.
Metal material jetting and binder jetting 3D printers
Material jetting 3D printers are equipped with various inkjet printheads (somewhat similar to 2D printing) that jet material onto a surface. The material then hardens, and another layer of “metal ink” is jetted on top.
Binder jetting is a similar process, but it is a binding agent that is jetted atop a layer of powder.
The Production System by Desktop Metal was designed for mass production. It is advertised by Desktop Metal as being a fast, cost-effective metal additive manufacturing solution, with a cost per part up to 20 times lower than with other metal 3D printing systems.
This Desktop Metal 3D printer is equipped with over 16,000 nozzles that are mounted onto a “print bar” that recoats the build plate with powder at the same time, hence explaining the technology’s name: Single Pass Jetting™.
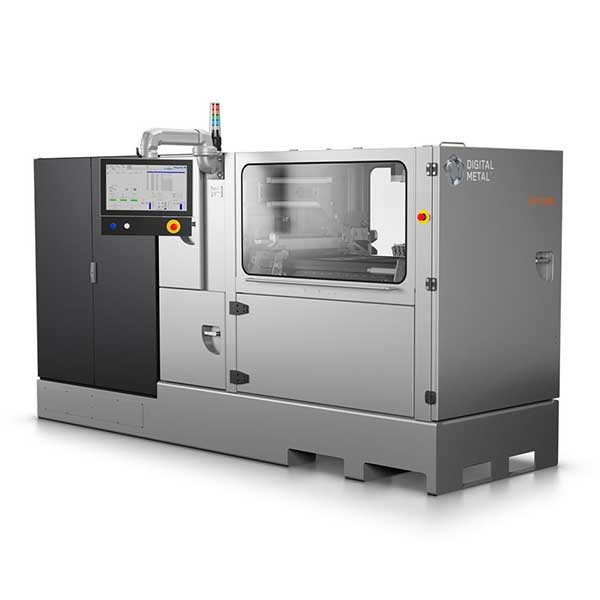
Digital Metal, a Höganäs Group company, creates incredibly detailed metal parts with their DM P2500 system. It is able to print 3D metal parts with an accuracy as high as 0.001mm (1µ), and with a medical-grade surface quality of around 0.006mm (6µ).
Another interesting feat to point out is that almost 100% of leftover powder can be recycled for future prints. This metal AM machine is able to churn out serial production series efficiently and reliably; one of the company’s first DM P2500 printers has been running 24/7 since 2013, according to Digital Metal.
The Digital Metal DM P2500 is a certified metal 3D printer (CE and UL) that is compatible with certified metal materials (ISO 22068).
Australian manufacturer SPEE3D has developed an impressively fast metal 3D printing technology called Supersonic Deposition. The technology is based on metal cold spray, using compressed air to “jet” metal powder through a nozzle at high speeds.
This enables the LightSPEE3D to 3D print at up to 100 grams per minute and with a range of metals including copper.
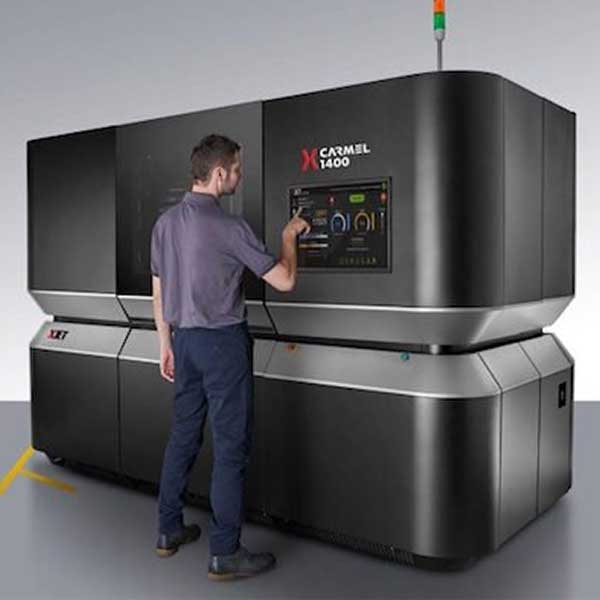
XJet developed an impressive, proprietary jetting technology they call NanoParticle Jetting™. This inkjet method disperses millions of tiny droplets that contain nanoparticles of solid metal. The liquid material comes in cartridges that are easy to insert into the printer.
After being printed, the metal parts must go through support removal and sintering processes to attain their final form.
DED: Directed Energy Deposition metal additive manufacturing systems
Directed Energy Deposition (DED) is comparable to filament extrusion. The metal material is pushed through a special nozzle, like with FFF/FDM, but a powerful laser beam solidifies the material at its deposition point.
Formalloy produces a range of metal DED 3D printers with up to 5 axes of motion. They can be used to produce metal parts but also to repair or clad existing parts.
Different laser wavelengths are available, as well as different build volumes: 200 x 200 x 200 mm, 500 x 500 x 500 mm, and 1000 x 1000 x 1000 mm. Metal 3D printers from Formalloy can be customized depending on company requirements.
Alternative metal 3D printers and special mentions
Hybrid metal manufacturing systems
Some manufacturers are specialized in hybrid metal manufacturing systems. They combine both subtractive and additive manufacturing methods, often with robotic arms that are able to move on more than three axes.
Some of the biggest actors on the hybrid metal AM system market are:
XXL-sized metal 3D printers for industrial production
For those that require very large metal parts, there are several huge, industrial machines that offer gigantic build volumes for industrial production. To name a few:
- Sciaky EBAM 300
- Titomic TKF1000
- ADC Aeroswift
- ADIRA AddCreator
- Fabrisonic SonicLayer 4000
- ExOne X1 160PRO
- InssTek MX-600
- BeAM Modulo 400
- Optomec Lens CS 600
- Additive Industries MetalFAB1
Metal 3D printers from China
There has recently been a lot of growth in the metal 3D printer market in Asia, and more specifically in China. Some Chinese brands have been upping their game in that respect, providing industrial-grade metal 3D printing options:
However, we feel that they are not yet playing in the same league as the 3D printers from our main selection, mostly due to a lack of distribution networks, after-sales service and training, and other factors which tend to matter when considering them together as a whole.
R&D metal 3D printers for labs
In certain cases, metal 3D printers are used for research purposes to develop and test new materials. There are a few machines that are specifically designed for this:
Pros and cons of metal 3D additive manufacturing
Benefits of 3D printing metal parts
- On-demand production: Metal additive manufacturing offers more flexibility and control over the production line.
- Complex designs made possible: With 3D printing technology, it is possible to create highly detailed and intricate parts that would have to be broken down into several pieces with traditional methods.
- Waste reduction: Compared to CNC milling, for example, metal AM produces much less waste as it only consumes the material needed for a certain part. This is more true for extrusion-based methods than it is for powder-based methods, where it isn’t always possible to re-use 100% of unsintered or unbinded material.
- Lighter parts: Whereas metal parts are usually completely solid infill-wise with other methods, 3D printing allows parts to be more or less hollow without undermining their strength and resistance.
- Cost-effectiveness: All the above benefits of metal 3D printing can inherently reduce costs per part, although high metal 3D printer prices do represent a significant entry barrier. Reaching a positive return on investment can take a while depending on your throughput.
Limits of metal 3D printing
- Metal 3D printing prices: Metal AM systems are still quite expensive, as are metal powders and metal filaments. There are hidden costs, too (e.g. energy consumption, learning curve, etc.).
- Environmental constraints and safety precautions: Most metal 3D printers have a large footprint and require specific operating environments with controlled temperatures, hygrometry, and more.
- Post-processing: In many cases it is necessary for parts to be post-processed, whether it’s debinding and sintering or finishing touches for surface quality.
- Physical properties: It can be difficult to achieve the same physical properties that traditionally manufactured metal parts have. There are a number of factors (e.g. anisotropy) to take into account during the design process and file preparation before even trying to 3D print a certain part.
Metal 3D printing materials
Which metals can you 3D print?
A growing number of metals and metal alloys can be 3D printed. These are the main ones:
- Aluminum
- Titanium
- Nickel, Inconel
- Copper
- Bronze
- Cobalt, Cobalt-Chrome
- Steels (tooling, maraging, stainless)
- Precious metals (gold, silver, platinum)
Which metal 3D printing material formats are available?
Metal 3D printing material can be found in various formats, catering to different metal 3D printing methods. The most common are:
- Powder
- Wire
- Filament
It is also possible to find metal 3D printing resin as well as metal sheets for lamination-based 3D printers.
Metal 3D printer price: how much does a metal 3D printer cost?
Industrial metal 3D printer prices generally range from about $30,000 to over one million dollars for the most premium, industrial-grade metal additive manufacturing systems.
Additional costs to consider are the materials for metal 3D printing, which can cost a few hundred USD/kg, as well as costs linked to post-processing (tools, time, etc.).
You may also like:
What’s the total cost of ownership for metal 3D printing?
Applications for metal AM systems
There are thousands of possibilities and use cases for metal 3D printing in a wide range of industries. A few industries have been incrementally using metal AM:
- Aerospace
- Automotive
- Medical
Whether it’s for tooling, replacement parts, or final products, many businesses can benefit from metal 3D printing.
However, metal additive manufacturing isn’t necessarily beneficial for every single metal part. Although some metal 3D printing systems have a relative capacity for serial production, it is generally cheaper to keep using traditional methods for simple parts.
For cases where complex geometries, rapid prototyping, and mass customization are required, metal AM is convenient and efficient.
Metal 3D printing services: order 3D metal parts online
For professionals with limited office space and human resources, low budgets, and/or few needs of custom parts and prototypes, metal 3D printing services can be an ideal solution.
These additive manufacturing service companies own a variety of high-quality 3D printers with different technologies, and their professionals are experts in 3D printing. It is possible to order metal 3D parts on-demand, without acquiring a 3D printer or having to buy a certain material for one-time use.
Here are some of the most trusted 3D printing service providers that offer metal printing services:
- Sculpteo
- Shapeways
- Hubs (ex 3D Hubs)
- Stratasys
- i.materialise
- Protolabs
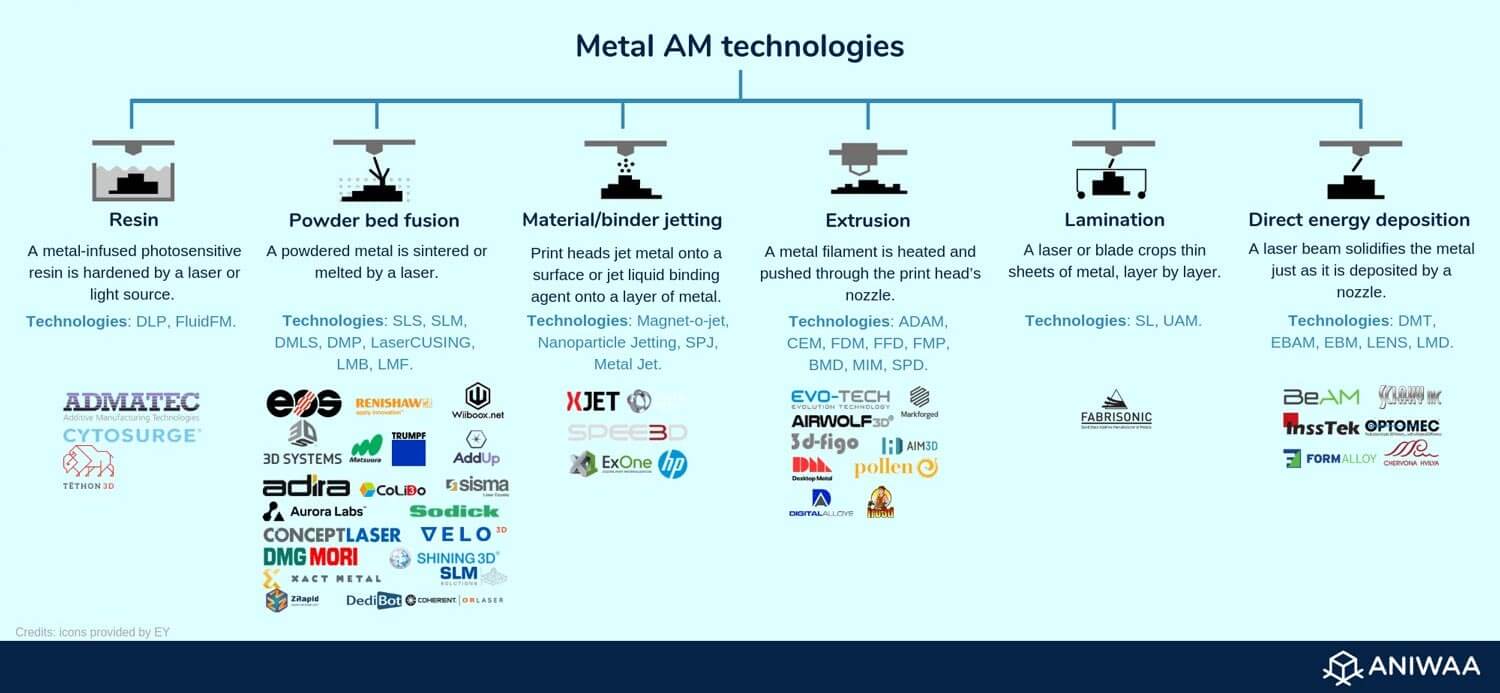
Metal 3D printing technologies and acronyms
Many manufacturers develop proprietary variations of existing technologies and label them their own registered names:
- Powder Bed Fusion (PBF): DMLS (Direct Metal Laser Sintering), DMP (Direct Metal Printing), LaserCUSING, LBM (Laser Beam Melting), LMF (Laser Metal Fusion), SLS (Selective Laser Sintering), SLM (Selective Laser Melting)
- Directed Energy Deposition (DED): DMT (Direct Metal Tooling), EBAM (Electron Beam Additive Manufacturing), EBM (Electron Beam Melting), LENS (Laser Engineered Net Shaping), LMD (Laser Metal Deposition)
- Metal Material Jetting (MJ) or Binder Jetting (BJ): Magnet-o-Jet, Nanoparticle Jetting, SPJ (Single Pass Jetting), Metal Jet
- Metal filament extrusion/Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF): ADAM (Atomic Diffusion Additive Manufacturing), CEM (Composite Extrusion Modeling), FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling), FFD (Fused Feedstock Deposition), FMP (Filament Metal Printing), BMD (Bound Metal Deposition), MIM (Metal Injection Molding)
- Lamination: SL (Sheet Lamination), UAM (Ultrasonic Additive Manufacturing)
- Metal resin 3D printing: DLP (Digital Light Processing), FluidFM, SLA (Stereolithography)
Metal 3D printing FAQ
Metal 3D printed parts can be as strong (or even stronger) as metal parts created with traditional manufacturing processes such as casting. The part’s strength will, however, depend on the metal AM method used and the conditions in which it is 3D printed.
Metal 3D printing became possible in the 1990s with the development of Selective Laser Melting technology. However, 3D metal printing only started to gain traction and public interest from around 2010 onwards.
There are several ways to 3D print metal. Layers of metal filament can be deposited one after the other, producing a green part that must later go through debinding and sintering steps. It is also possible to fuse metal powder particles together with a laser, or with an inkjet printhead that deposits drops of binding material onto the powder.
 English
English  Français
Français




















